题目:Synergistic immobilization of ions in mixed tin-lead and all-perovskite tandem solar cells
作者:Yuhui Liu1,2#, Tianshu Ma1,2#, Changlei Wang1,2*, Zhenhai Yang1,2*, Yue Zhao1,2, Zhanghao Wu1,2, Chen Chen1,2, Yining Bao1,2, Yuhang Zhai1,2, Tianci Jia1,2, Cong Chen3, Dewei Zhao3* and Xiaofeng Li1,2*
单位:
1School of Optoelectronic Science and Engineering & Collaborative Innovation Center of Suzhou Nano Science and Technology, Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, China
2Key Lab of Advanced Optical Manufacturing Technologies of Jiangsu Province & Key Lab of Modern Optical Technologies of Education Ministry of China, Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, China
3College of Materials Science and Engineering & Engineering Research Center of Alternative Energy Materials & Devices of Ministry of Education, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610065, China
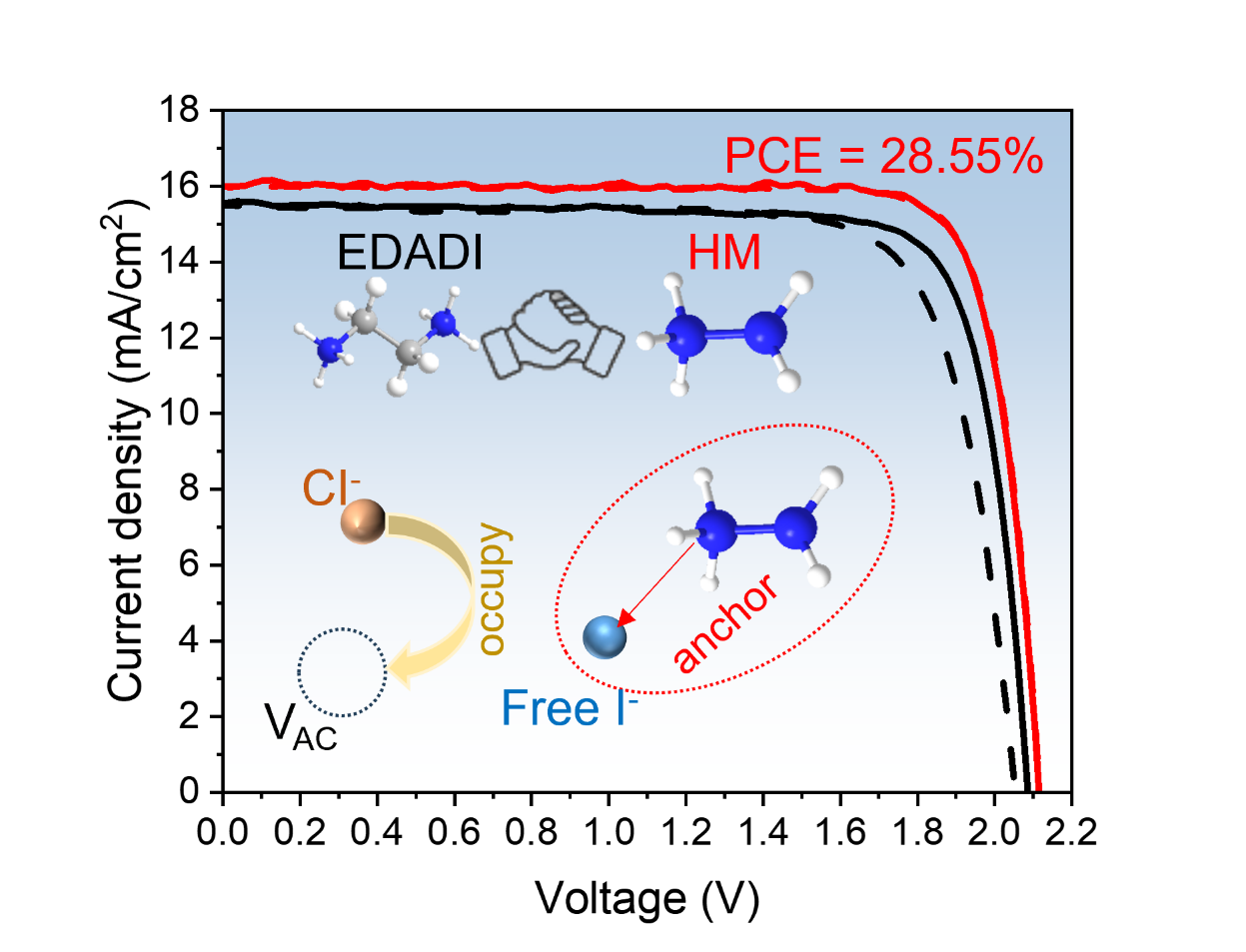
Abstract:Low-bandgap (LBG) mixed tin-lead (SnPb) perovskite solar cells (PSCs) suffer from inferior performance due to their high defect density. Conventionally, ethylenediammonium diiodide (EDADI) is used as a surface passivator to reduce defects and improve device photovoltaic performance, but it introduces severe hysteresis caused by excessive mobilized ions at the top interface. Here, we report a mobile ion suppressing strategy of using hydrazine monohydrochloride (HM) as a bulk passivator to anchor the free ions in LBG perovskites. The protonated hydrazine (N2H5+) of HM formed hydrogen bonds with iodine (I–) ions, while the chloride (Cl–) ions occupied the I– vacancies, collectively impeding the migration of I– and thus mitigating the ion movement-induced hysteresis that arose from EDADI usage. The synergistic strategy of HM doping and EDADI post-treatment significantly suppresses the oxidation of Sn2+, decreases trap density, and inhibits rapid crystallization of perovskite. Consequently, we achieved a champion efficiency of 23.21% for LBG PSCs. Integrating these cells with wide-bandgap PSCs into all-perovskite tandem solar cells yields a high efficiency of 28.55% (certified 28.31%) with negligible hysteresis.
摘要:锡铅混合(Sn-Pb)窄带隙钙钛矿太阳能电池(PSCs)因缺陷密度高而导致性能不佳。传统工作通常采用乙二胺碘(EDADI)作为表面钝化材料来减少缺陷以提升器件的光伏性能,但该材料会在顶部界面引发过量的离子迁移,导致严重的回滞现象。本文报道了一种抑制离子迁移的新策略,即采用盐酸肼(HM)作为体钝化剂锚定窄带隙钙钛矿中的游离离子。HM中的质子化肼(N2H5+)与碘离子(I–)形成氢键,同时氯离子(Cl–)占据I–空位,协同阻碍了I–迁移,从而有效缓解了EDADI引发的离子迁移型回滞问题。HM掺杂与EDADI后处理的协同策略显著抑制了Sn2+氧化,降低了陷阱密度,并延缓了钙钛矿的快速结晶。最终,本研究制备了高性能的窄带隙钙钛矿太阳能电池,最高效率达到23.21%。将其与宽带隙子电池结合构建全钙钛矿叠层太阳能电池,获得了28.55%的高效率(认证效率为28.31%),且回滞现象可忽略不计。
影响因子:16.6
链接://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-58810-6.
